Ankle Injury Physical Therapy NYC
ActiveCare Physical Therapy Midtown NYC
The most common injury in the ankle is the ankle sprain. It is typically an inversion sprain where the toes roll down and toward the inside and the person falls over sideways. An ankle sprain refers to tears in the ligament.
The ankle joint is the smallest of the three main joints of the leg. The ankle is a mortise joint with the large talar bone as its base, and the tibia and fibula above and to the side of it. It is a fairly mobile joint with support from many surrounding ligaments. The inside of the joint has greater support with 5 ligaments. The outside of the joint has lesser with only 3, leading to more injury in this area.
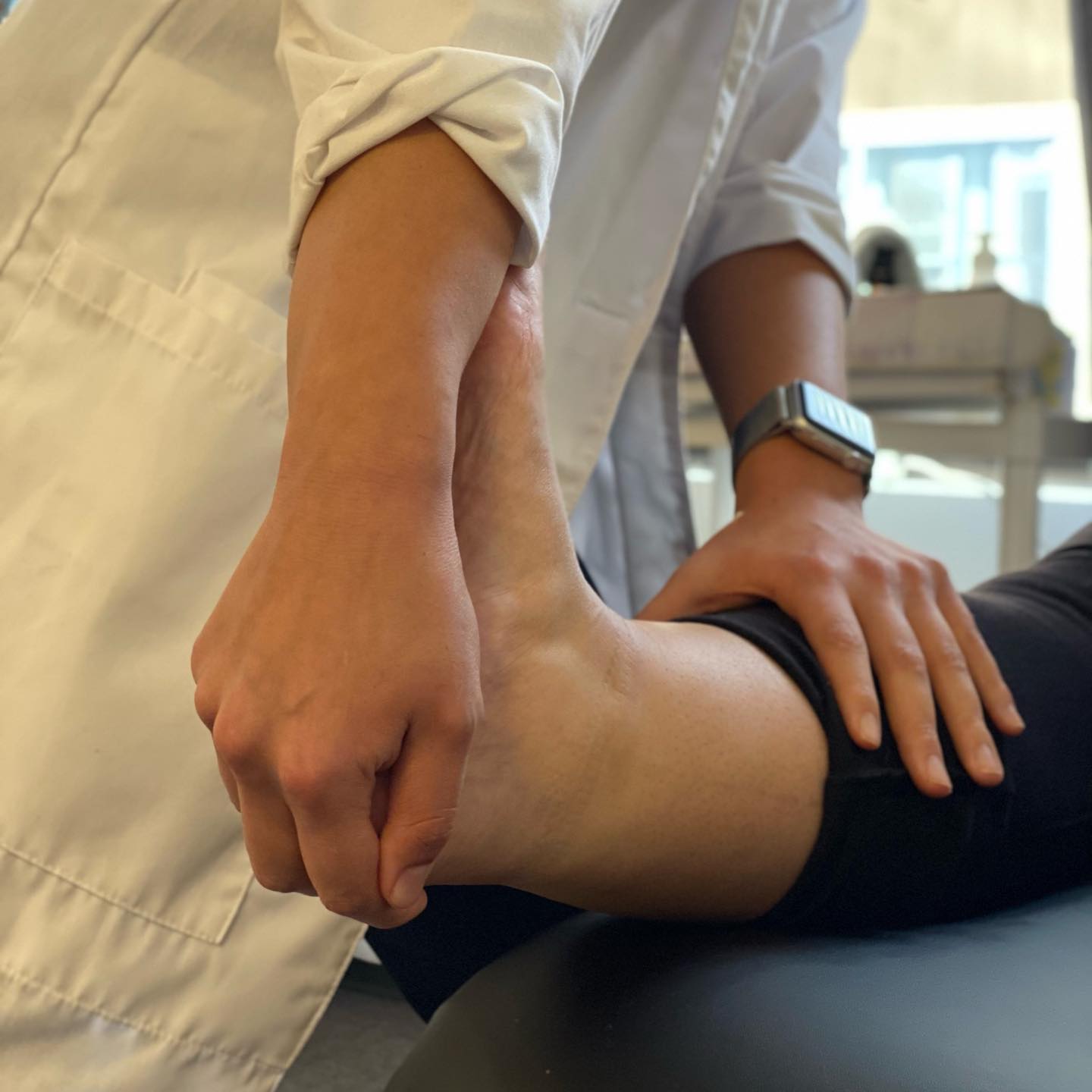
The technique demonstrated is an anterior posterior joint mobilization of the fibula on the talus. The function of this is to push the fibular bone back to restore full range of motion in the joint. After an inversion sprain, the fibula gets pulled forward resulting in a malalignment of the joint as well as a restriction of dorsiflexion (pulling the toes up toward the head) because the tibia and fibula cannot move up and out during this motion.
Our Approach
Skilled Joint Mobilizations
- The patient is lying on her back.
- The therapist is at the patient’s feet, facing the head of the patient.
- The therapist places the heel of the outside hand on the fibula. This is the stabilizing force.
- The other hand grasps the mid-foot around the arch. This is the mobilizing force.
- The fibula is held back as the mobilizing hand inverts the talus restoring the fibula back to its normal resting position.
Graston Technique ®
- Patient and therapist positioning as above.
- The therapist chooses a Graston instrument to work on the front of the ankle to loosen the connective tissues.
- The other hand stabilizes the ankle/foot complex.
- The soft tissue mobilization allows for full toe up and toe down positioning to help restore normal ankle joint mechanics.










.jpg)



